Medical
About Us


Our Fields
Gastric Cancer Risk Assessment Test (ABCD classification) is a method for determining the health status of the stomach of an individual by means of a combination of a pepsinogen test (as a gastric mucosal atrophy marker) and a Helicobacter pylori antibody test for screening H. pylori infections (considered to be the main cause of gastric ulcers, duodenal ulcers, and gastric cancers).
It is a blood test designed to objectively evaluate the health status (degree of mucosal atrophy) of the stomach by measuring the serum concentration of a substance called “pepsinogen”. Many gastric cancer cases are shown to develop subsequent to gastric mucosal atrophy, the extent of which can be estimated using the pepsinogen test, and the test results can be utilized to screen individuals for increased risk of gastric cancer.
It is a screening test of H. pylori infections of gastric mucosa. When infected with H. pylori, the body produces antibodies against H. pylori (H. pylori antibodies) which are released into the blood. This antibody test is a method for measuring these H. pylori antibodies in the blood of the individual.
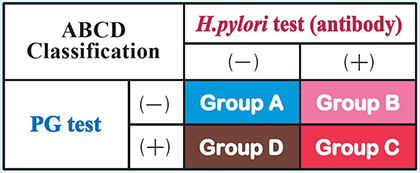
Group A: The gastric mucosa is generally healthy and there is a low risk for gastric diseases. Caution should be exercised to distinguish H. pylori infections from diseases unrelated to H. pylori such as reflux esophagitis. It is likely that individuals in Group A are not infected with H. pylori but some may have existing or previous H. pylori infections. It is preferable that such individuals undergo imaging tests including endoscopy at least once.
Group B: The gastric mucosa is somewhat damaged. Caution should be exercised to distinguish between gastric ulcers and duodenal ulcers. These individuals also have an increased risk of developing gastric cancer. An endoscopic examination is recommended. H. pylori eradication therapy is also usually recommended.
Group C: The gastric mucosa is clearly damaged and exhibit advanced atrophy. The individuals have high risk for developing gastric cancer. Regular endoscopic examinations are recommended. H. pylori eradication therapy is also recommended.
Group D: The gastric mucosa is considered as highly advanced atrophy. The individuals have extremely high risk for affecting diseases such as gastric cancer. Examination for the presence of H. pylori infection is recommended. Ensure that the individuals undergo disease visualization examinations, such as endoscopy, and that the individuals consult a physician at a specialized medical institution.
Caution in interpreting the PG test should be used for individuals who;
Note: ABCD risk classification is the primarily test to stratify the risk for gastric cancer and should be clearly distinguished from gastric cancer screening that is performed to determine the exist or absence of gastric cancer. It is essential to properly inform individuals about the necessity of undergoing appropriate imaging tests such as endoscopy and stomach X-ray for diagnosis of organic diseases, such as gastric cancer.